So, how much does a Formula 1 car weigh? 798 kilograms (1,759 lbs) in total, which is 3 kg more than the initial 795 kg restriction that teams reportedly find difficult to reach.
Table of Contents
- 1 The Importance of Weight and Balance in F1 Racing
- 2 Formula 1 Car Components and Their Weights
- 3 F1 weight through the years
- 4 Weight of the F1 drivers
- 5 The Effects of Weight Limits on F1 Car Performance and Design
- 6 Technological Advances and Their Impact on Formula 1 Car Weight
- 7 Weight Management Strategies for Drivers and Teams
- 8 The Evolution of F1 Car Weight Regulations Over the Years
- 9 Comparing Formula 1 Car Weight to Other Motorsports
The Importance of Weight and Balance in F1 Racing
For a multitude of reasons, weight is important in the realm of Formula 1 racing.
First off, a lighter automobile will perform better on the track since it will usually be faster and more agile.
Additionally, a vehicle’s balance, which in turn affects handling and stability during high-speed cornering, is influenced by the distribution of weight across the vehicle.
The FIA has set a minimum weight limit for F1 teams to adhere to, but they also have to optimize their vehicles for “burstiness”—having a mix of lightweight and heavyweight components to boost balance and performance.
Teams carefully analyze the building materials they utilize and continually tweak their car designs to reach the ideal weight-to-strength ratio in order to remain competitive.
Formula 1 Car Components and Their Weights
Formula 1 cars have a large number of parts, and the weight of each item affects the car’s overall performance significantly.
Following are some typical components and an estimate of their weights:
| Engine | Minimum 331lbs (150kg) |
| Fuel | Maximum 242lbs (110kg) |
| Front wing | Around 22lbs (10kg) |
| Chassis/Monocoque | No set weight |
| Halo | 15 lbs (7kg) |
| Gearbox | Around 88lbs (40kg) |
| Steering wheel | Around 2.8lbs (1.3kg) |
Teams put forth a lot of effort to lighten these components without sacrificing their dependability or structural integrity.
Teams can construct cars that are both lightweight and robust enough to handle the demands of Formula 1 racing using contemporary materials and production methods.
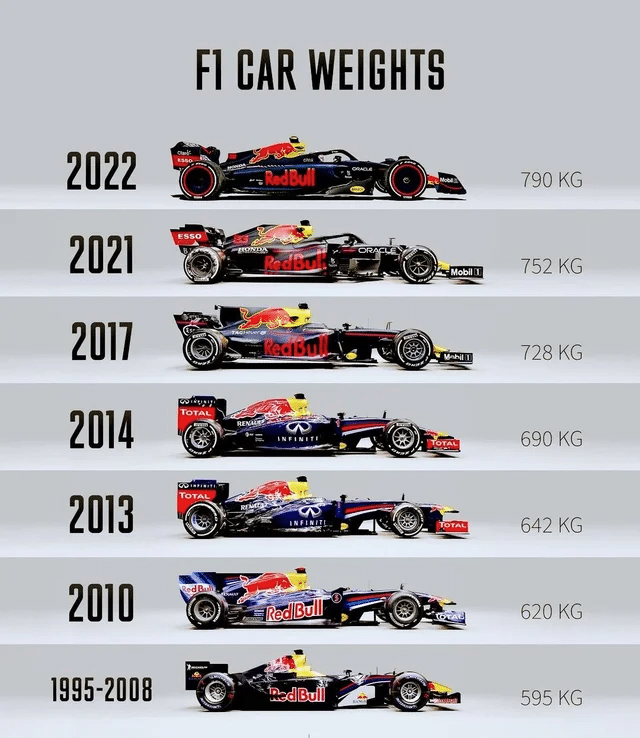
F1 weight through the years
Since safety laws required the introduction of safety equipment like the halo, the 2022 cars are now without a doubt the heaviest in Formula One history. Additionally, the prohibition on refueling led to bigger and heavier cars.
| Year | Weight | Changes |
| 2009 | 1333 lbs (605kg) | |
| 2010 | 1366 lbs (620kg) | Refuelling is banned |
| 2011 | 1410 lbs (640kg) | |
| 2012 | 1410 lbs (640kg) | |
| 2013 | 1415 lbs (642kg) | |
| 2014 | 1523 lbs (691kg) | Hybrid V6 engines introduced |
| 2015 | 1548 lbs (702kg) | Anti-intrusion panels added to cockpit |
| 2016 | 1548 lbs (702kg) | |
| 2017 | 1604 lbs (728kg) | Wider wheels and tyres introduced |
| 2018 | 1618 lbs (734kg) | Halo added to the car |
| 2019 | 1638 lbs (743kg) | 176lbs (80kg) driver allowance |
| 2020 | 1644 lbs (746kg) | Second fuel flow meter added |
| 2021 | 1657 lbs (752kg) | |
| 2022 | 1766 lbs (801kg) | Larger wheels and wheel coverings were also launched along with new cars built around ground effects aerodynamics. |
| 2023 | 1759 lbs (798kg) | |
| 2024 | 1759 lbs (798kg) |
Weight of the F1 drivers
The drivers’ physique differs. As a result, they are of varying weights. Since Alex Albon is the tallest and Yuki Tsunoda is the shortest driver, their weights naturally vary.
The drivers must also weigh a certain amount according to FIA regulations. They need to be 80 kg. If not, the cockpit will receive the ballast instead.
There is nowhere else in the car where you can put this. The driver’s helmet, shoes, and race suit are all part of the 80kg.
In order to prevent shorter drivers from having an edge over taller ones, this rule was put into effect in 2019.
| DRIVER | WEIGHT |
| Alex Albon | 163lbs (74kg) |
| Lewis Hamilton | 161lbs (73kg) |
| Logan Sargeant | 156lbs (71kg) |
| Max Verstappen | 159lbs (72kg) |
| George Russell | 154lbs (70kg) |
| Pierre Gasly | 154lbs (70kg) |
| Lance Stroll | 154lbs (70kg) |
| Charles Leclerc | 152lbs (69kg) |
| Valtteri Bottas | 152lbs (69kg) |
| Kevin Magnussen | 150lbs (68kg) |
| Lando Norris | 150lbs (68kg) |
| Fernando Alonso | 150lbs (68kg) |
| Nico Hulkenberg | 163lbs (74kg) |
| Esteban Ocon | 145.5lbs (66kg) |
| Daniel Ricciardo | 145.5lbs (66kg) |
| Carlos Sainz | 141lbs (64kg) |
| Guanyu Zhou | 139lbs (63kg) |
| Sergio Perez | 139lbs (63kg) |
| Oscar Piastri | 149lbs (68kg) |
| Yuki Tsunoda | 119lbs (54kg) |
The drivers did not have a distinct weight prior to the introduction of the overall car weight. The teams had the opportunity to improve on the balance of the car to meet the total car weight requirements.
Now, things have changed. Leveling the playing field is the goal of Formula 1.
The Effects of Weight Limits on F1 Car Performance and Design
The FIA establishes a minimum weight restriction for Formula 1 cars, as was already mentioned.
The minimum weight is set at 798 kg (1,759 lbs) for the 2023 season.
This restriction forces design teams to concentrate on creating cars that meet this criteria while yet offering the best performance possible.
Meeting this minimum need, however, is not always simple because technology developments can result in heavier components, such as complicated hybrid power units or newer, safer tires.
Teams can carefully put ballast, or extra weight, when a car’s weight is getting close to the minimal limit to improve balance and performance.
Anywhere on the car can be used as ballast, giving teams the ability to modify the center of gravity and fine-tune handling characteristics to suit the requirements of each racing circuit.
Technological Advances and Their Impact on Formula 1 Car Weight
Both good and negative effects of technology have been seen on the weight of Formula 1 cars.
On the one hand, advancements in manufacturing processes and materials science have made it possible for groups to create components that are lighter and stronger.
For instance, the weight of the chassis has been greatly decreased when compared to traditional materials thanks to the usage of carbon fiber composite components.
On the other hand, some technological improvements have made people heavier.
Examples include the deployment of safety elements like the halo and the introduction of hybrid power units.
For teams to maintain peak performance as the sport develops and prioritizes safety and sustainability, they must strike a balance between these technical advancements and weight-reduction initiatives.
Weight Management Strategies for Drivers and Teams
Different tactics are used by drivers and teams to control and optimize car weight.
To keep within a certain weight range, drivers frequently follow stringent diet and exercise plans. This is because lighter drivers can perform better in terms of vehicle balance.
Throughout the design and development process, teams frequently study and optimize car weight and balance using sophisticated software and simulations.
In order to maintain the perfect balance for shifting track conditions, they may also modify different car parameters during races, like as downforce amounts or suspension settings.
The Evolution of F1 Car Weight Regulations Over the Years
The weight restrictions for Formula 1 cars have drastically altered throughout time to account for changing objectives and technological advancements in the sport.
For instance, early F1 vehicles weighed roughly 500 kg in the 1960s, which was a significant reduction.
Regulations that required more stringent safety measures and the introduction of hybrid powertrains ultimately resulted in these vehicles becoming heavier.
Despite these modifications, the FIA still enforces minimum weight rules to maintain fairness and control team performance levels.
The continual search for the ideal harmony between speed, safety, and competition within the sport is reflected in the evolution of these rules.
Comparing Formula 1 Car Weight to Other Motorsports
Formula 1 cars are often lighter and more maneuverable when compared to vehicles used in other disciplines like NASCAR or IndyCar.
For instance, IndyCars weigh roughly 720 kg (1,590 lbs) without gasoline and the driver, while NASCAR stock cars often weigh around 1,500 kg (about 3,300 lbs).
These distinctions highlight the special opportunities and challenges connected with optimizing weight in Formula 1. These variances result from the various design philosophies, materials, and technology employed in each racing.