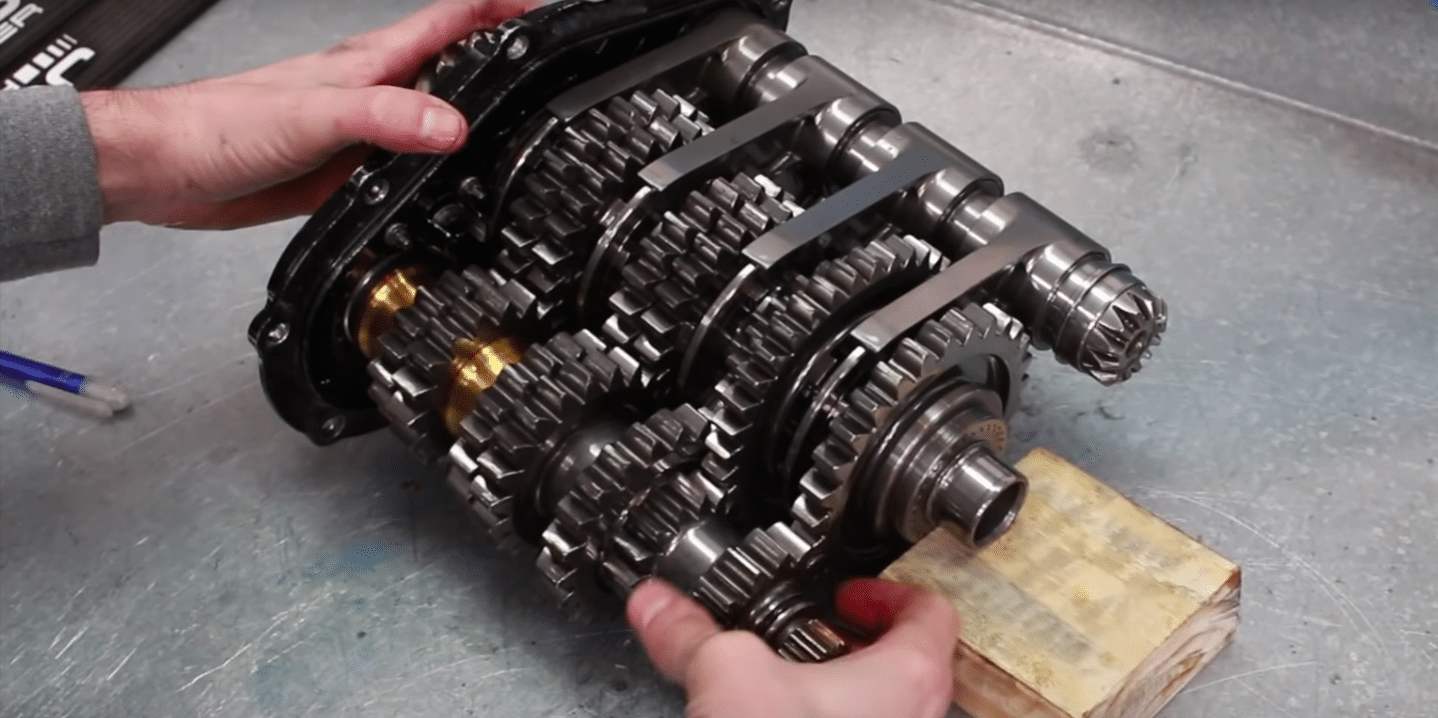
Since the 2014 season, F1 cars have been equipped with eight forward gears and one reverse gear. This configuration allows the cars to achieve impressive speeds and acceleration while maintaining fuel efficiency and adhering to FIA regulations.
The eight forward gears enable the cars to reach top speeds of over 360 km/h, with the highest recorded speed being 378.035 km/h during qualifying for the European Grand Prix in 2016. The single reverse gear, although rarely used, is a necessary component for safety purposes and is standardized by the FIA.
It’s worth noting that the number of gears in an F1 car is not directly proportional to its power output. Instead, the gearbox design focuses on optimizing the power-to-weight ratio and maximizing aerodynamic efficiency to achieve the best possible performance on the track.
Table of Contents
- 1 Understanding the F1 Gearbox System
- 2 The Role of Semi-Automatic Paddle Shifters
- 3 Gear Regulations and Limitations in F1 Racing
- 4 The Art of Selecting Gear Ratios
- 5 The Challenge of Maintaining an F1 Transmission
- 6 Debunking Myths: Common Misconceptions about F1 Gears
- 7 A Glimpse into the Top Performing F1 Teams and Their Gear Strategies
Understanding the F1 Gearbox System
The gearbox in an F1 car is one of the most complicated and expensive components, costing upwards of $600,000. It is a highly automated semi-automatic sequential gearbox that allows for quick and precise gear shifts.
The gearbox system is designed to withstand the extreme forces generated by the car’s high-speed cornering and rapid acceleration. F1 drivers can perform over 2,000 gear changes in a single race, highlighting the importance of a reliable and efficient gearbox system.
The FIA imposes stringent guidelines on gearboxes, allowing only four gearbox changes per season. This regulation challenges teams to design and maintain gearbox systems that can endure the rigors of an entire season with minimal issues.
The Role of Semi-Automatic Paddle Shifters
Contemporary F1 cars utilize semi-automatic paddle shifters mounted behind the steering wheel for quick and efficient gear changes. This system eliminates the need for a manual gear stick and clutch pedal, allowing drivers to keep both hands on the wheel and maintain better control of the car.
The paddle shifters work in tandem with the car’s electronic control unit (ECU) to ensure smooth and precise gear shifts. When a driver pulls on the paddle, the ECU momentarily cuts power to the engine, disengages the clutch, and selects the desired gear. This process happens in a matter of milliseconds, minimizing the loss of power and momentum during gear changes.
Gear Regulations and Limitations in F1 Racing
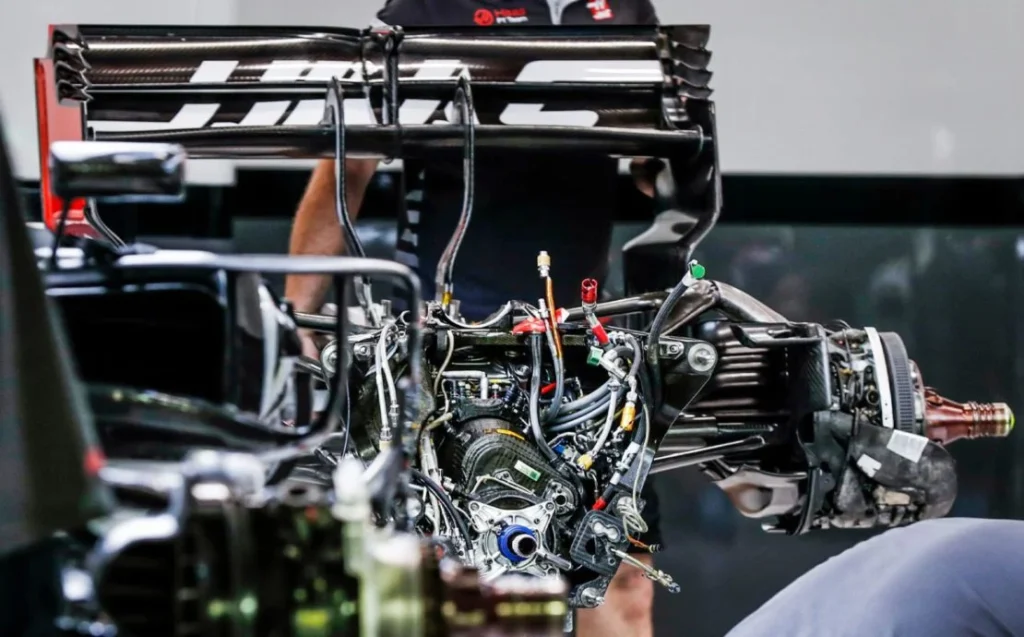
The FIA, the governing body for Formula One, imposes various regulations on gearboxes to ensure fair competition and driver safety. One such regulation is the limitation on gearbox changes, as mentioned earlier, with teams being allowed only four changes per season.
Another regulation concerns the reverse gear, which must be available and functional in the car. Although it is rarely used, the reverse gear plays a crucial role in safety situations, such as when a car needs to be moved out of a dangerous position on the track.
The FIA also regulates the design and construction of gearboxes to prevent teams from gaining an unfair advantage. This includes restrictions on materials, weight, and dimensions, as well as mandating the use of certain components to maintain consistency across teams.
The Art of Selecting Gear Ratios
Gear ratios play a crucial role in determining an F1 car’s performance on the track. Teams meticulously analyze each circuit to establish the best gear ratios for their vehicles, taking into account factors such as straight-line speed, cornering forces, and engine performance.
The optimal gear ratio allows the car to achieve the highest possible speed while maintaining engine performance within the ideal power band. This balance is crucial for maximizing acceleration and minimizing lap times.
F1 teams use sophisticated software and simulations to model various gear ratio configurations and determine the most effective setup for each race. This process requires a deep understanding of the car’s aerodynamics, engine performance, and driver preferences, as well as the unique characteristics of each track.
The Challenge of Maintaining an F1 Transmission
The gearbox must be able to withstand high-speed cornering, rapid acceleration, and frequent gear changes, all while maintaining optimal performance and reliability.
Teams employ specialized engineers and technicians to monitor, maintain, and repair the gearbox systems. Regular inspections and preventive maintenance are crucial to ensuring the longevity and performance of the gearbox throughout the season.
In addition to routine maintenance, teams must also be prepared to address any unexpected issues or failures that may arise during a race weekend. This requires a deep understanding of the gearbox system and the ability to quickly diagnose and resolve problems under pressure.
Debunking Myths: Common Misconceptions about F1 Gears
A basic misconception is that more gears automatically equate to more power. While having additional gears can help optimize engine performance and fuel efficiency, it does not directly increase the power output of the engine. The key to maximizing performance lies in finding the optimal gear ratio for each track and balancing the power-to-weight ratio and aerodynamic efficiency.
Lastly, some people believe that F1 cars do not have a clutch. While it is true that drivers do not engage the clutch using a traditional pedal, F1 cars do have a clutch system that is controlled electronically. This system works in conjunction with the paddle shifters to facilitate quick and smooth gear changes.
A Glimpse into the Top Performing F1 Teams and Their Gear Strategies
Top-performing F1 teams, such as Mercedes, Ferrari, and Red Bull, invest significant resources into developing and optimizing their gearbox systems. These teams employ some of the best engineers and technicians in the industry to design, build, and maintain their gearboxes, ensuring they remain at the forefront of racing technology.
Each team has its unique approach to gear strategies, taking into account factors such as driver preferences, engine performance, and track characteristics. Some teams may prioritize straight-line speed, while others focus on cornering performance or fuel efficiency.
The gear strategies employed by these top teams are constantly evolving, as they seek to gain any possible advantage over their competitors. By pushing the boundaries of gearbox technology and optimizing their gear ratios for each race, these teams continue to set the standard for performance and innovation in Formula One.