Since 1950, when Formula One (F1) first debuted as a well-liked sport, many improvements have taken place, especially in terms of safety and effectiveness.
One such modification was the addition of tail lights to F1 vehicles.
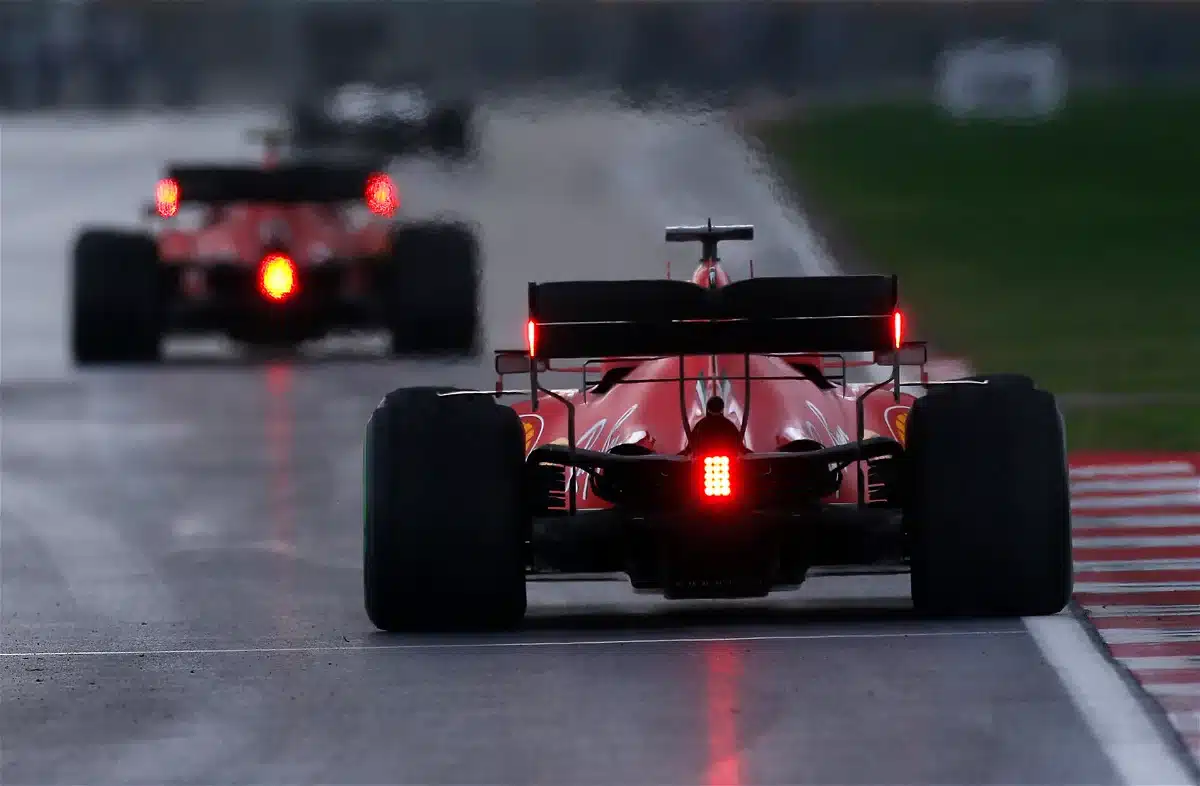
Driver safety on the racetrack is greatly aided by rear lights, particularly the red blinking light.
We’ll talk about the function of these flashing red lights and how they affect Formula One racing in this article.
Understanding the Role of the Red Flashing Light in Racing Conditions
The red flashing light on the back of an F1 car has two main functions: to increase visibility in rainy weather and to signal when the vehicle’s Energy Recovery System is harvesting energy (ERS).
Since 2014, this light has been a crucial component of F1 cars, guaranteeing that drivers can see one another in bad weather and during energy-harvesting periods.
Visibility can become extremely limited while driving in pouring rain, which raises the possibility of accidents.
F1 drivers do not benefit from windscreen wipers or other road users traveling at slower speeds, although casual drivers like you and I do.
By making vehicles more visible during races and enhancing overall safety, the red flashing light on the back of F1 cars aids in resolving this issue.
How Wet Weather Affects Visibility and Safety in F1 Racing
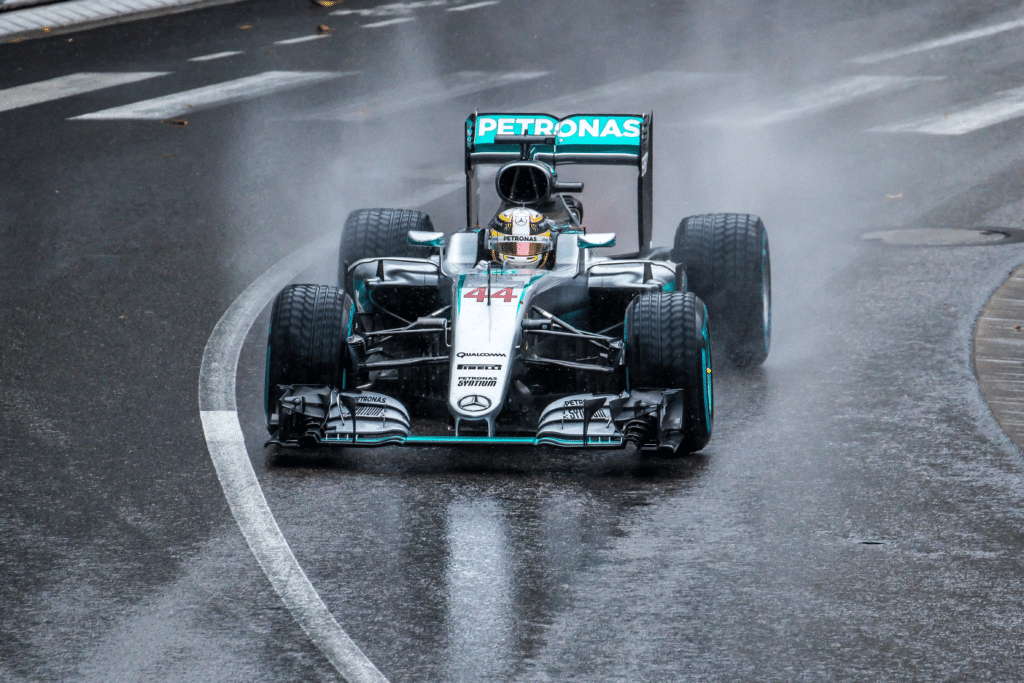
In wet weather, the spray produced by an F1 car moving quickly might cause the driver behind to become temporarily blinded.
Because of this, drivers occasionally have to veer onto separate racing lanes in order to see what is happening in front of them.
By enabling drivers to plainly see other vehicles even in bad weather, the flashing red light dramatically increases visibility.
F1 cars have two additional red lights on the back of the rear wing in addition to the flashing red light to improve visibility.
When racing in wet conditions, these lights are significantly less obvious until they are activated, yet they are extremely important for assuring driver safety.
The Energy Harvesting Process and Its Connection to Rear Lights
The red flashing light on the back of F1 cars, as was already mentioned, also functions as a signal for when energy harvesting is happening.
The ERS system in F1 cars transforms thermal energy from exhaust fumes and kinetic energy from braking into electrical energy.
Both the Motor Generator Unit-Kinetic (MGU-K) and the Motor Generator Unit-Heat are involved in this process (MGU-H).
The red light flashes to alert other drivers that energy harvesting may be taking place and that the automobile may be moving a little more slowly than usual.
This alert is essential because it enables motorists to identify when a vehicle in front of them is engaging in energy harvesting, which may force them to briefly slow down.
Without this warning, a driver could unintentionally collide with the back of the vehicle in front, which could cause an accident.
Debunking Myths: Is the Red Flashing Light a Brake Light?
The red flashing light on the back of F1 cars is sometimes misunderstood to mean the vehicle is braking.
Contrary to popular opinion, F1 cars lack brake lights found on other types of vehicles.
As drivers are aware of their own personal braking limits and the performance potential of their vehicles, brake lights are useless in F1 racing.
Also, the braking point of an F1 car is not fixed due to variable tire strategy and varying grip levels.
Thus, brake lights wouldn’t give drivers behind any meaningful information.

Exploring Other Light Functions in F1 Cars
F1 cars also have green back lights in addition to the red flashing light.
These green lights signify that the driver is inexperienced and does not yet possess a Super License, which is necessary to compete in Formula 1 races.
The green light makes it easier for other drivers to identify and take into account the varying degrees of experience of their fellow competitors, creating a safer racing environment.
The Importance of Rear Lights in Ensuring Driver Safety
Particularly in inclement weather and energy harvesting, F1 rear lights are essential for ensuring driver safety.
Whether they are red or green, these signals aid drivers in keeping an eye on other cars on the track and preventing potential collisions.
The likelihood of accidents happening during races would be much higher without these back lights.
Unique F1 Lighting Designs and Innovations
Formula One consistently pushes the frontier of innovation, and this can be seen in the way that the lighting systems on the F1 cars are designed.
For instance, to handle grueling racing conditions, the power of the original rear light was boosted from 15W to 21W in 1983.
Also, for the rear lights to be at the driver’s eye level, they must be placed just 30 cm off the ground.
Similar rear light designs have been used onto certain road cars, like the Ferrari 488 and LaFerrari, demonstrating the influence of F1 innovation on regular cars.
The Vital Role of Red Blinking Lights in F1 Racing
Red blinking lights on F1 cars are a crucial component of driver safety, enhancing visibility in bad weather and indicating energy-harvesting activities.
We can grasp the significance of such safety measures in high-stakes racing conditions by knowing the function of these lights.
The significance of these innovations and their potential to revolutionize automotive safety and efficiency are attested to by the continuous evolution of F1 car designs and their influence on conventional vehicles.





